|
|
| |
 |
BADIMINTON |
 |
|
|
Badminton is a racquet sport played by either two opposing players (singles) or two opposing pairs (doubles), who take positions on opposite halves of a rectangular court that is divided by a net. Players score points by striking a shuttlecock with their racquet so that it passes over the net and lands in their opponents' half of the court. A rally ends once the shuttlecock has struck the ground, and the shuttlecock may only be struck once by each side before it passes over the net.
The shuttlecock is a feathered projectile whose unique aerodynamic properties cause it to fly differently from the balls used in most racquet sports; in particular, the feathers create much higher drag, causing the shuttlecock to decelerate more rapidly than a ball. Because shuttlecock flight is strongly affected by wind, competitive badminton is always played indoors. Badminton is also played outdoors as a casual recreational activity, often as a garden or beach game
Badminton is an Olympic sport with five competitive disciplines: men's and women's singles, men's and women's doubles, and mixed doubles, in which each pair is a man and a woman. At high levels of play, the sport demands excellent fitness: players require aerobic stamina, strength, and speed. It is also a technical sport, requiring good motor coordination and the development of sophisticated racket skills.
|
 |
|
| |
History and development
Badminton was known in ancient times; an early form of the sport was played in ancient Greece and Egypt. In Japan, the related game Hanetsuki was played as early as the 16th century. In the west, badminton came from a game called battledore and shuttlecock, in which two or more players keep a feathered shuttlecock in the air with small racquets. The game was called "Poona" in India during the 18th century, and British Army officers stationed there took a competitive Indian version back to England in the 1860s, where it was played at country houses as an upper class amusement. Isaac Spratt, a London toy dealer, published a booklet, "Badminton Battledore - a new game" in 1860, but unfortunately no copy has survived.
The new sport was definitively launched in 1873 at the Badminton House, Gloucestershire, owned by the Duke of Beaufort. During that time, the game was referred to as "The Game of Badminton," and, the game's official name became Badminton.
Until 1887 the sport was played in England under the rules that prevailed in India. The Bath Badminton Club standardized the rules and made the game applicable to English ideas. The basic regulations were drawn up in 1887. In 1893, the Badminton Association of England published the first set of rules according to these regulations, similar to today's rules, and officially launched badminton in a house called "Dunbar" at 6 Waverley Grove, Portsmouth, England on September 13 of that year. They also started the All England Open Badminton Championships, the first badminton competition in the world, in 1899.
The Badminton World Federation (BWF) was established in 1934 with Canada, Denmark, England, France, the Netherlands, Ireland, New Zealand, Scotland, and Wales as its founding members. India joined as an affiliate in 1936. The BWF now governs international badminton and develops the sport globally.
While originated in England, international badminton has traditionally been dominated by a few Asian countries, plus Denmark from Europe. China, Indonesia, South Korea and Malaysia are among the nations that have consistently produced world-class players in the past few decades and dominated competitions on the international level, with China being the most dominant in recent years. |
| |
Laws of the game
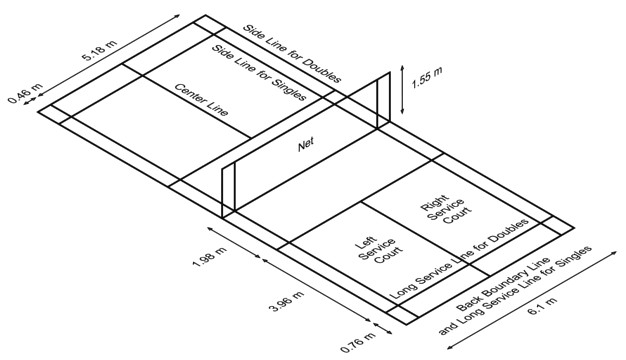
The court is rectangular and divided into halves by a net. Courts are almost always marked for both singles and doubles play, although the laws permit a court to be marked for singles only. The doubles court is wider than the singles court, but both are the same length. The exception, which often causes confusion to newer players is the doubles court has a shorter serve-length dimension
The full width of the court is 6.1 metres (20 ft), and in singles this width is reduced to 5.18 metres (17 ft). The full length of the court is 13.4 metres (44 ft). The service courts are marked by a centre line dividing the width of the court, by a short service line at a distance of 1.98 metres (6.5 ft) from the net, and by the outer side and back boundaries. In doubles, the service court is also marked by a long service line, which is 0.78 metres (2 ft 6 inch) from the back boundary.
The net is 1.55 metres (5 ft 1 inch) high at the edges and 1.524 metres (5 ft) high in the centre. The net posts are placed over the doubles side lines, even when singles is played.
There is no mention in the Laws of badminton, of a minimum height for the ceiling above the court. Nonetheless, a badminton court will not be suitable if the ceiling is likely to be hit on a high serve.
|
| |
 |
Scoring system and service
The scoring system changed in May 2006. For more information, see Scoring System Development of Badminton.
The basics
Each game is played up to 21 points, with players scoring a point whenever they win a rally (this differs from the old system, where players could only win a point on their serve). A match is the best of three games.
|
|
| |
At the start of the rally, the server and receiver stand in diagonally opposite service courts (see court dimensions). The server hits the shuttlecock so that it would land in the receiver's service court. This is similar to tennis, except that a badminton serve must be hit from below the waist in underhand form (upwards), the shuttlecock is not allowed to bounce, and in tennis the players stand outside their service courts.
In singles, the server stands in his right service court when his score is even, and in his left service court when his score is odd
In doubles, if the serving side wins a rally, the same player continues to serve, but he changes service courts so that he serves to each opponent in turn. When the serving side loses a rally, the serve passes to their opponents (unlike the old system, there is no "second serve"). If their new score is even, the player in the right service court serves; if odd, the player in the left service court serves. The players' service courts are determined by their positions at the start of the previous rally, not by where they were standing at the end of the rally.
A consequence of this system is that, each time a side regain the service, the server will be the player who did not serve last time.
When the server serves, the shuttlecock must pass over the short service line on the opponents' court or it will count as a fault.
If the score reaches 20-all, then the game continues until one side gains a two point lead (such as 24-22), up to a maximum of 30 points (30-29 is a winning score).
At the start of a match a coin is tossed. The winners of the coin toss may choose whether to serve or receive first, or they may choose which end of the court they wish to occupy. Their opponents make the remaining choice. In less formal settings, the coin toss is often replaced by hitting a shuttlecock into the air: whichever side it points to serves first.
In subsequent games, the winners of the previous game serve first. For the first rally of any doubles game, the serving pair may decide who serves and the receiving pair may decide who receives. The players change ends at the start of the second game; if the match reaches a third game, they change ends both at the start of the game and when the leading pair's score reaches 11 points.
The server and receiver must remain within their service courts, without touching the boundary lines, until the server strikes the shuttlecock. The other two players may stand wherever they wish, so long as they do not unsight the opposing server or receiver.
Faults
Players win a rally by striking the shuttlecock onto the floor within the boundaries of their opponents' court. Players also win a rally if their opponents commit a fault. The most common fault in badminton is when the players fail to return the shuttlecock so that it passes over the net and lands inside their opponents' court, but there are also other ways that players may be faulted. The following information lists some of the more common faults.
Several faults pertain specifically to service. A serving player shall be faulted if he strikes the shuttlecock from above his waist (defined as his lowest rib), or if his racket is not pointing downwards at the moment of impact. This particular law was modified in 2006: previously, the server's racket had to be pointing downwards to the extent that the racket head was below the hand holding the racket; and now, any angle below the horizontal is acceptable.
Neither the server nor the receiver may lift a foot until the shuttlecock has been struck by the server. The server must also initially hit the base (cork) of the shuttlecock, although he may afterwards also hit the feathers as part of the same stroke. This law was introduced to ban an extremely effective service style known as the S-serve or Sidek serve, which allowed the server to make the shuttlecock spin chaotically in flight.
Each side may only strike the shuttlecock once before it passes back over the net; but during a single stroke movement, a player may contact a shuttlecock twice (this happens in some sliced shots). A player may not, however, hit the shuttlecock once and then hit it with a new movement, nor may he carry and sling the shuttlecock on his racket. It is a fault if the shuttlecock hits the ceiling.
Lets
If a let is called, the rally is stopped and replayed with no change to the score. Lets may occur due to some unexpected disturbance such as a shuttlecock landing on court (having been hit there by players on an adjacent court).
If the receiver is not ready when the service is delivered, a let shall be called; yet if the receiver makes any attempt to return the shuttlecock, he shall be judged to have been ready. There is no let if the shuttlecock hits the tape (even on service). |
| |
Governing bodies
The Badminton World Federation (BWF) is the internationally recognized governing body of the sport. The BWF headquarters are currently located in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
Five regional confederations are associated with the BWF:
- Asia: Badminton Asia Confederation (BAC)
- Africa: Badminton Confederation of Africa (BCA)
- Americas: Badminton Pan Am (North America and South America belong to the same confederation; BPA)
- Europe: Badminton Europe (BE)
- Oceania: Badminton Oceania (BO)
|
 |
|
Equipment
Rackets
Badminton rackets are light, with top quality rackets weighing between about 70 and 100 grams (without strings). They are composed of many different materials ranging from carbon fibre composite (graphite reinforced plastic) to solid steel, which may be augmented by a variety of materials. Carbon fibre has an excellent strength to weight ratio, is stiff, and gives excellent kinetic energy transfer. Before the adoption of carbon fibre composite, rackets were made of light metals such as aluminium. Earlier still, rackets were made of wood. Cheap rackets are still often made of metal, but wooden rackets are no longer manufactured for the ordinary market, due to their excessive weight and cost.
There is a wide variety of racket designs, although the racket size and shape are limited by the Laws. Different rackets have playing characteristics that appeal to different players. The traditional oval head shape is still available, but an isometric head shape is increasingly common in new rackets.
Strings
Badminton strings are thin, high performing strings in the range of about 0.65 to 0.73 millimeters thickness. Thicker strings are more durable, but many players prefer the feel of thinner strings. String tension is normally in the range of 18 to 36 lbf (80 to 130 newtons). Recreational players generally string at lower tensions than professionals, typically between 18 and 25 lbf (110 N). Professionals string between about 25 and 36 lbf (160 N).
Grip
The choice of grip allows a player to increase the thickness of his racket handle and choose a comfortable surface to hold. A player may build up the handle with one or several grips before applying the final layer. There are two main types of grip: replacement grips and overgrips. Replacement grips are thicker, and are often used to increase the size of the handle. Overgrips are thinner (less than 1 mm), and are often used as the final layer
Shuttlecock
A shuttlecock (often abbreviated to shuttle and also known as a bird or birdie) is a high-drag projectile, with an open conical shape: the cone is formed from sixteen overlapping goose feathers embedded into a rounded cork base. The cork is covered with thin leather.
Shuttles with a plastic skirt are often used by recreational players to reduce their costs as feathered shuttles break easily.
A shuttlecock weighs around 4.75 - 5.50 grams. It has 14-16 feathers with each feather 70mm in length. The diameter of the cork is 25-28mm and the diameter of the circle that the feathers make is around 54mm.
Strokes
Badminton offers a wide variety of basic strokes, and players require a high level of skill to perform all of them effectively. All strokes can be played either forehand or backhand (except for the high serve, which is only ever played as a forehand). A player's forehand side is the same side as his playing hand: for a right-handed player, the forehand side is his right side and the backhand side is his left side. Forehand strokes are hit with the front of the hand leading (like hitting with the palm), whereas backhand strokes are hit with the back of the hand leading (like hitting with the knuckles). Players frequently play certain strokes on the forehand side with a backhand hitting action, and vice-versa.
In the forecourt and midcourt, most strokes can be played equally effectively on either the forehand or backhand side; but in the rearcourt, players will attempt to play as many strokes as possible on their forehands, often preferring to play a round-the-head forehand overhead (a forehand "on the backhand side") rather than attempt a backhand overhead. Playing a backhand overhead has two main disadvantages. First, the player must turn his back to his opponents, restricting his view of them and the court. Second, backhand overheads cannot be hit with as much power as forehands: the hitting action is limited by the shoulder joint, which permits a much greater range of movement for a forehand overhead than for a backhand. The backhand clear is considered by most players and coaches to be the most difficult basic stroke in the game, since precise technique is needed in order to muster enough power for the shuttlecock to travel the full length of the court. For the same reason, backhand smashes tend to be weak.
The choice of stroke depends on how near the shuttlecock is to the net, and whether it is above net height: players have much better attacking options if they can reach the shuttlecock well above net height, especially if it is also close to the net. In the forecourt, a high shuttlecock will be met with a net kill, hitting it steeply downwards and attempting to win the rally immediately. In the midcourt, a high shuttlecock will usually be met with a powerful smash, also hitting downwards and hoping for an outright winner or a weak reply. Athletic jump smashes, where players jump upwards for a steeper smash angle, are a common and spectacular element of elite men's doubles play. In the rearcourt, players strive to hit the shuttlecock while it is still above them, rather than allowing it to drop lower. This overhead hitting allows them to play smashes, clears (hitting the shuttlecock high and to the back of the opponents' court), and dropshots (hitting the shuttlecock so that it falls softly downwards into the opponents' forecourt). If the shuttlecock has dropped lower, then a smash is impossible and a full-length, high clear is difficult.
When the shuttlecock is well below net height, players have no choice but to hit upwards. Lifts, where the shuttlecock is hit upwards to the back of the opponents' court, can be played from all parts of the court. If a player does not lift, his only remaining option is to push the shuttlecock softly back to the net: in the forecourt this is called a netshot; in the midcourt or rearcourt, it is often called a push or block.
When the shuttlecock is near to net height, players can hit drives, which travel flat and rapidly over the net into the opponents' rear midcourt and rearcourt. Pushes may also be hit flatter, placing the shuttlecock into the front midcourt. Drives and pushes may be played from the midcourt or forecourt, and are most often used in doubles: they are an attempt to regain the attack, rather than choosing to lift the shuttlecock and defend against smashes. After a successful drive or push, the opponents will often be forced to lift the shuttlecock.
When defending against a smash, players have three basic options: lift, block, or drive. In singles, a block to the net is the most common reply. In doubles, a lift is the safest option but it usually allows the opponents to continue smashing; blocks and drives are counter-attacking strokes, but may be intercepted by the smasher's partner. Many players use a backhand hitting action for returning smashes on both the forehand and backhand sides, because backhands are more effective than forehands at covering smashes directed to the body.
The service presents its own array of stroke choices. Unlike in tennis, the serve is restricted by the Laws so that it must be hit upwards. The server can choose a low serve into the forecourt (like a push), or a lift to the back of the service court, or a flat drive serve. Lifted serves may be either high serves, where the shuttlecock is lifted so high that it falls almost vertically at the back of the court, or flick serves, where the shuttlecock is lifted to a lesser height but falls sooner.
Once players have mastered these basic strokes, they can hit the shuttlecock from and to any part of the court, powerfully and softly as required. Beyond the basics, however, badminton offers rich potential for advanced stroke skills that provide a competitive advantage. Because badminton players have to cover a short distance as quickly as possible, the purpose of many advanced strokes is to deceive the opponent, so that either he is tricked into believing that a different stroke is being played, or he is forced to delay his movement until he actually sees the shuttle's direction. "Deception" in badminton is often used in both of these senses. When a player is genuinely deceived, he will often lose the point immediately because he cannot change his direction quickly enough to reach the shuttlecock. Experienced players will be aware of the trick and cautious not to move too early, but the attempted deception is still useful because it forces the opponent to delay his movement slightly. Against weaker players whose intended strokes are obvious, an experienced player will move before the shuttlecock has been hit, anticipating the stroke to gain an advantage.
Slicing and using a shortened hitting action are the two main technical devices that facilitate deception. Slicing involves hitting the shuttlecock with an angled racket face, causing it to travel in a different direction than suggested by the body or arm movement. Slicing also causes the shuttlecock to travel much slower than the arm movement suggests. For example, a good crosscourt sliced dropshot will use a hitting action that suggests a straight clear or smash, deceiving the opponent about both the power and direction of the shuttlecock. A more sophisticated slicing action involves brushing the strings around the shuttlecock during the hit, in order to make the shuttlecock spin. This can be used to improve the shuttle's trajectory, by making it dip more rapidly as it passes the net; for example, a sliced low serve can travel slightly faster than a normal low serve, yet land on the same spot. Spinning the shuttlecock is also used to create spinning netshots (also called tumbling netshots), in which the shuttlecock turns over itself several times (tumbles) before stabilizing; sometimes the shuttlecock remains inverted instead of tumbling. The main advantage of a spinning netshot is that the opponent will be unwilling to address the shuttlecock until it has stopped tumbling, since hitting the feathers will result in an unpredictable stroke. Spinning netshots are especially important for high level singles players.
The lightness of modern rackets allows players to use a very short hitting action for many strokes, thereby maintaining the option to hit a powerful or a soft stroke until the last possible moment. For example, a singles player may hold his racket ready for a netshot, but then flick the shuttlecock to the back instead with a shallow lift. This makes the opponent's task of covering the whole court much more difficult than if the lift was hit with a bigger, obvious swing. A short hitting action is not only useful for deception: it also allows the player to hit powerful strokes when he has no time for a big arm swing. The use of grip tightening is crucial to these techniques, and is often described as finger power. Elite players develop finger power to the extent that they can hit some power strokes, such as net kills, with less than a 10 cm racket swing.
It is also possible to reverse this style of deception, by suggesting a powerful stroke before slowing down the hitting action to play a soft stroke. In general, this latter style of deception is more common in the rearcourt (for example, dropshots disguised as smashes), whereas the former style is more common in the forecourt and midcourt (for example, lifts disguised as netshots).
Deception is not limited to slicing and short hitting actions. Players may also use double motion, where they make an initial racket movement in one direction before withdrawing the racket to hit in another direction. This is typically used to suggest a crosscourt angle but then play the stroke straight, or vice-versa. Triple motion is also possible, but this is very rare in actual play. An alternative to double motion is to use a racket head fake, where the initial motion is continued but the racket is turned during the hit. This produces a smaller change in direction, but does not require as much time.
|
Competitions
The BWF organizes several international competitions, including the Thomas Cup, the premier men's event, and the Uber Cup, the women's equivalent. The competitions take place once every two years. More than 50 national teams compete in qualifying tournaments within continental confederations for a place in the finals. The final tournament involves 12 teams, following an increase from eight teams in 2004.
The Sudirman Cup, a mixed team event held once every two years, began in 1989. It is divided into seven groups based on the performance of each country. To win the tournament, a country must perform well across all five disciplines (men's doubles and singles, women's doubles and singles, and mixed doubles). Like soccer, it features a promotion and relegation system in every group.
Individual competition in badminton was a demonstration event in the 1972 and 1988 Summer Olympics. It became a Summer Olympics sport at the Barcelona Olympics in 1992. The 32 highest ranked badminton players in the world participate in the competition, and each country submitting three players to take part. In the BWF World Championships, only the highest ranked 64 players in the world, and a maximum of three from each country, can participate in any category.
All these tournaments, along with the BWF World Junior Championships, are level one tournaments.
At the start of 2007, the BWF also introduce a new tournament structure: the BWF Super Series. This level two tournament will stage 12 open tournaments around the world with 32 players (half the previous limit). The players collect points that determine whether they can play in Super Series Final held at the year end.
Level three tournaments will consist of Grand Prix Gold and Grand Prix. Top players can collect the world ranking points and enable them to play in the BWF Super Series open tournaments. These include the regional competitions in Asia (Badminton Asia Championships) and Europe (European Badminton Championships), which produce the world's best players as well as the Pan America Badminton Championships.
The level four tournaments, known as International Challenge, International Series and Future Series, encourages participation by junior players. |
| |
|
|
|
|